28 KiB
Bibliotecas Principales de Java
Programando con Objects y String
-
Los packages sirven para organizar nuestro código.
-
Los packages son parte del FQN (Full Qualified Name) de la clase.
-
El nombre completo de la clase (FQN) consta de: PACKAGE.NOMBRE_SIMPLE_DE_LA_CLASE
-
La definición de package debe ser la primera declaración en el código fuente
-
Para facilitar el uso de clases de otros packages, podemos importarlas
-
Los import son justo después de la declaración del package
-
La nomenclatura padrón es usar el nombre de dominio en la web al revés con el nombre del proyecto, por ejemplo:
pe.com.caelum.gargarus br.com.alura.notas cl.gov.reg.news us.com.linode.miapp
Reestructurando proyecto bytebank
Proyecto bytebank
📂️ bibliotecas
└── 📂️ bytebank
├── 📁️ bin
└── 📂️ src
├── 📂️ com.bytebank
│ ├── 📂️ com.bytebank.modelo
│ │ ├── ☕️ Administrador.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ Autenticable.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ AutenticacionUtil.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ Cliente.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ Contador.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ ControlBonificacion.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ Cuenta.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ CuentaAhorro.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ CuentaCorriente.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ Funcionario.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ Gerente.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ SistemaInterno.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ TestControlBonificacion.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ TestCuentas.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ TestFuncionario.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ TestGerente.java
│ │ ├── ☕️ TestReferencias.java
│ │ └── ☕️ TestSistemaInterno.java
│ └── 📂️ com.bytebank.test
│ ├── ☕️ TestControlBonificacion.java
│ ├── ☕️ TestCuentas.java
│ ├── ☕️ TestFuncionario.java
│ ├── ☕️ TestGerente.java
│ ├── ☕️ TestReferencias.java
│ └── ☕️ TestSistemaInterno.java
└── 📄️ module-info.java
Imports entre paquetes, Administrador.java
package com.bytebank.modelo;
public class Administrador extends Funcionario implements Autenticable {
...
package com.bytebank.test;
import com.bytebank.modelo.CuentaCorriente;
import com.bytebank.modelo.CuentaAhorro;
public class TestCuentas {
...
Modificadores de accesos
Mas a menos restrictivo:
| Keyword | Descripción |
|---|---|
private |
visible solo dentro de la clase |
<<package private>> |
visible dentro de la clase y dentro del mismo paquete (default) |
protected |
visible dentro de la clase, del packete y para las cualquier hijo |
public |
visible desde cualquier paquete |
Note
Pueden ser usados en la definición de la clase, atributo, constructor y método.
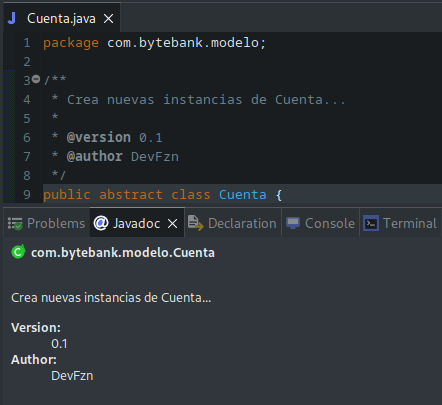
Javadoc
Comentarios en java
/*
* Bloque Comentario
*/
// Comentario en una linea
Javadoc
/**
*
* @author (usado en la clase o interfaz)
* @version (usado en la clase o interfaz)
* @param (usado en el método y constructor)
* @return (usado solo en el método)
* @exception o @throws (en el método o constructor)
* @see
* @since
* @serial
* @deprecated
*/
Clase Cuenta.java
/**
* Instancia una Cuenta, sin parametros
*/
public Cuenta() {}
/**
* Instancia una Cuenta usando agencia y numero
* @param agencia
* @param numero
*/
public Cuenta(int agencia, int numero) {
...
/**
* Retira saldo de la cuenta, si no hay saldo suficiente arroja excepción
* @param valorRetiro
* @throws SaldoInsuficienteException
*/
public void retirar(double valorRetiro) throws SaldoInsuficienteException {
...
Se puede generar el Javadoc en Eclipse en la barra principal -> Project -> @Generate Javadoc
Exportar jar
Se exporta el proyecto anterior: bytebank_libreria.jar
Se crea un nuevo proyecto bytebank_libreria,
donde se crea un directorio lib/ a nivel de src/ y bin/. Luego se agregar el
archivo jar en el Build Path, para poder usar sus packetes.
Creación de package test y clase TestLibreria
com.bytebank.test.TestLibreria.java
package com.bytebank.test;
import com.bytebank.modelo.Cuenta;
import com.bytebank.modelo.CuentaCorriente;
public class TestLibreria {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cuenta cuenta = new CuentaCorriente(10, 20);
cuenta.depositar(500);
System.out.println(cuenta.getSaldo());
}
}
Jar Ejecutable
Es un archivo .jar igual al anterior, con la diferencia que este incluye un punto
de entrada método main en el archivo MANIFEST.MF, punto donde se inicia el
programa.
El ejecutable bytebank_ejecutable.jar , tiene como punto de entrada TestLibreria.java
Note
Revisar la opciones de exportación para incluir o no código fuente del paquete y/o del JDK.
package com.bytebank.test;
import com.bytebank.modelo.Cuenta;
import com.bytebank.modelo.CuentaCorriente;
public class TestLibreria {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cuenta cuenta = new CuentaCorriente(10, 20);
cuenta.depositar(500);
System.out.println(cuenta.getSaldo());
}
}
Salida
java -jar bytebank_ejecutable.jar
Cuentas creadas: 1
500.0
Maven
Java es una plataforma de desarrollo completa que destaca por su gran cantidad de proyectos de código abierto (open source). Para la mayoría de problemas en el día a día del desarrollador ya existen librerías para solucionar. Es decir, si te gustaría conectarte con una base de datos, o trabajar en desarrollo web, en el área de ciencia de datos, creación de servicios o Android, ya existen librerías para esto, muchas veces más de una.
Existe la necesidad de organizar, centralizar y versionar los JARs de esas librerías y administrar las dependencias entre ellos. Para solucionar esto, se crearon herramientas específicas y en el mundo Java se destacó Maven. Maven organiza los JARs (código compilado, código fuente y documentación) en un repositorio central que es público y se puede buscar.
Apache: maven in 5 minutes.
tldr mvn
mvn
Apache Maven.
Tool for building and managing Java-based projects.
More information: https://maven.apache.org.
- Compile a project:
mvn compile
- Compile and package the compiled code in its distributable format, such as a `jar`:
mvn package
- Compile and package, skipping unit tests:
mvn package -DskipTests
- Install the built package in local maven repository. (This will invoke the compile and package commands too):
mvn install
- Delete build artifacts from the target directory:
mvn clean
- Do a clean and then invoke the package phase:
mvn clean package
- Clean and then package the code with a given build profile:
mvn clean -Pprofile package
- Run a class with a main method:
mvn exec:java -Dexec.mainClass="com.example.Main" -Dexec.args="arg1 arg2"
mvn --help
usage: mvn [options] [<goal(s)>] [<phase(s)>]
Options:
-am,--also-make If project list is specified, also
build projects required by the
list
-amd,--also-make-dependents If project list is specified, also
build projects that depend on
projects on the list
-B,--batch-mode Run in non-interactive (batch)
mode (disables output color)
-b,--builder <arg> The id of the build strategy to
use
-C,--strict-checksums Fail the build if checksums don't
match
-c,--lax-checksums Warn if checksums don't match
--color <arg> Defines the color mode of the
output. Supported are 'auto',
'always', 'never'.
-cpu,--check-plugin-updates Ineffective, only kept for
backward compatibility
-D,--define <arg> Define a system property
-e,--errors Produce execution error messages
-emp,--encrypt-master-password <arg> Encrypt master security password
-ep,--encrypt-password <arg> Encrypt server password
-f,--file <arg> Force the use of an alternate POM
file (or directory with pom.xml)
-fae,--fail-at-end Only fail the build afterwards;
allow all non-impacted builds to
continue
-ff,--fail-fast Stop at first failure in
reactorized builds
-fn,--fail-never NEVER fail the build, regardless
of project result
-gs,--global-settings <arg> Alternate path for the global
settings file
-gt,--global-toolchains <arg> Alternate path for the global
toolchains file
-h,--help Display help information
-l,--log-file <arg> Log file where all build output
will go (disables output color)
-llr,--legacy-local-repository Use Maven 2 Legacy Local
Repository behaviour, ie no use of
_remote.repositories. Can also be
activated by using
-Dmaven.legacyLocalRepo=true
-N,--non-recursive Do not recurse into sub-projects
-npr,--no-plugin-registry Ineffective, only kept for
backward compatibility
-npu,--no-plugin-updates Ineffective, only kept for
backward compatibility
-nsu,--no-snapshot-updates Suppress SNAPSHOT updates
-ntp,--no-transfer-progress Do not display transfer progress
when downloading or uploading
-o,--offline Work offline
-P,--activate-profiles <arg> Comma-delimited list of profiles
to activate
-pl,--projects <arg> Comma-delimited list of specified
reactor projects to build instead
of all projects. A project can be
specified by [groupId]:artifactId
or by its relative path
-q,--quiet Quiet output - only show errors
-rf,--resume-from <arg> Resume reactor from specified
project
-s,--settings <arg> Alternate path for the user
settings file
-t,--toolchains <arg> Alternate path for the user
toolchains file
-T,--threads <arg> Thread count, for instance 2.0C
where C is core multiplied
-U,--update-snapshots Forces a check for missing
releases and updated snapshots on
remote repositories
-up,--update-plugins Ineffective, only kept for
backward compatibility
-v,--version Display version information
-V,--show-version Display version information
WITHOUT stopping build
-X,--debug Produce execution debug output
java.lang
java.lang
es la base de lenguaje, sus métodos, objs, etc. Están a disposición sin necesidad
de importarlos. Por ejemplo el
String
// String nombre = new String("DevFzn");
// java.lang.String nombre = "DevFzn";
String nombre = "DevFzn";
String
Los Strings son inmutables, TestString.java
String nombre = "DevFzn";
//nombre.replace = ('D', 'd');
nombre = nombre.replace('D', 'd');
//nombre.concat(" estudiando en Alura");
nombre = nombre.concat(" estudiando con Alura");
Métodos String
JDK 17
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| char | charAt(int index) | Returns the char value at the specified index. |
| IntStream | chars() | Returns a stream of int zero-extending the char values from this sequence. |
| int | codePointAt(int index) | Returns the character (Unicode code point) at the specified index. |
| int | codePointBefore(int index) | Returns the character (Unicode code point) before the specified index. |
| int | codePointCount(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | Returns the number of Unicode code points in the specified text range of this String. |
| IntStream | codePoints() | Returns a stream of code point values from this sequence. |
| int | compareTo(String anotherString) | Compares two strings lexicographically. |
| int | compareToIgnoreCase(String str) | Compares two strings lexicographically, ignoring case differences. |
| String | concat(String str) | Concatenates the specified string to the end of this string. |
| boolean | contains(CharSequence s) | Returns true if and only if this string contains the specified sequence of char values. |
| boolean | contentEquals(CharSequence cs) | Compares this string to the specified CharSequence. |
| boolean | contentEquals(StringBuffer sb) | Compares this string to the specified StringBuffer. |
| static String | copyValueOf(char[] data) | Equivalent to valueOf(char[]). |
| static String | copyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count) | Equivalent to valueOf(char[], int, int). |
| Optional | describeConstable() | Returns an Optional containing the nominal descriptor for this instance, which is the instance itself. |
| boolean | endsWith(String suffix) | Tests if this string ends with the specified suffix. |
| boolean | equals(Object anObject) | Compares this string to the specified object. |
| boolean | equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) | Compares this String to another String, ignoring case considerations. |
| static String | format(String format, Object... args) | Returns a formatted string using the specified format string and arguments. |
| static String | format(Locale l, String format, Object... args) | Returns a formatted string using the specified locale, format string, and arguments. |
| String | formatted(Object... args) | Formats using this string as the format string, and the supplied arguments. |
| byte[] | getBytes() | Encodes this String into a sequence of bytes using the platform's default charset, storing the result into a new byte array. |
| void | getBytes(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, byte[] dst, int dstBegin) | Deprecated. This method does not properly convert characters into bytes. |
| byte[] | getBytes(String charsetName) | Encodes this String into a sequence of bytes using the named charset, storing the result into a new byte array. |
| byte[] | getBytes(Charset charset) | Encodes this String into a sequence of bytes using the given charset, storing the result into a new byte array. |
| void | getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) | Copies characters from this string into the destination character array. |
| int | hashCode() | Returns a hash code for this string. |
| String | indent(int n) | Adjusts the indentation of each line of this string based on the value of n, and normalizes line termination characters. |
| int | indexOf(int ch) | Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character. |
| int | indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character, starting the search at the specified index. |
| int | indexOf(String str) | Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring. |
| int | indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring, starting at the specified index. |
| String | intern() | Returns a canonical representation for the string object. |
| boolean | isBlank() | Returns true if the string is empty or contains only white space codepoints, otherwise false. |
| boolean | isEmpty() | Returns true if, and only if, length() is 0. |
| static String | join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence... elements) | Returns a new String composed of copies of the CharSequence elements joined together with a copy of the specified delimiter. |
| static String | join(CharSequence delimiter, Iterable<? extends CharSequence> elements) | Returns a new String composed of copies of the CharSequence elements joined together with a copy of the specified delimiter. |
| int | lastIndexOf(int ch) | Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified character. |
| int | lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified character, searching backward starting at the specified index. |
| int | lastIndexOf(String str) | Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified substring. |
| int | lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified substring, searching backward starting at the specified index. |
| int | length() | Returns the length of this string. |
| Stream | lines() | Returns a stream of lines extracted from this string, separated by line terminators. |
| boolean | matches(String regex) | Tells whether or not this string matches the given regular expression. |
| int | offsetByCodePoints(int index, int codePointOffset) | Returns the index within this String that is offset from the given index by codePointOffset code points. |
| boolean | regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len) | Tests if two string regions are equal. |
| boolean | regionMatches(int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len) | Tests if two string regions are equal. |
| String | repeat(int count) | Returns a string whose value is the concatenation of this string repeated count times. |
| String | replace(char oldChar, char newChar) | Returns a string resulting from replacing all occurrences of oldChar in this string with newChar. |
| String | replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) | Replaces each substring of this string that matches the literal target sequence with the specified literal replacement sequence. |
| String | replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) | Replaces each substring of this string that matches the given regular expression with the given replacement. |
| String | replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) | Replaces the first substring of this string that matches the given regular expression with the given replacement. |
| String | resolveConstantDesc(MethodHandles.Lookup lookup) | Resolves this instance as a ConstantDesc, the result of which is the instance itself. |
| String[] | split(String regex) | Splits this string around matches of the given regular expression. |
| String[] | split(String regex, int limit) | Splits this string around matches of the given regular expression. |
| boolean | startsWith(String prefix) | Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix. |
| boolean | startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) | Tests if the substring of this string beginning at the specified index starts with the specified prefix. |
| String | strip() | Returns a string whose value is this string, with all leading and trailing white space removed. |
| String | stripIndent() | Returns a string whose value is this string, with incidental white space removed from the beginning and end of every line. |
| String | stripLeading() | Returns a string whose value is this string, with all leading white space removed. |
| String | stripTrailing() | Returns a string whose value is this string, with all trailing white space removed. |
| CharSequence | subSequence(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | Returns a character sequence that is a subsequence of this sequence. |
| String | substring(int beginIndex) | Returns a string that is a substring of this string. |
| String | substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | Returns a string that is a substring of this string. |
| char[] | toCharArray() | Converts this string to a new character array. |
| String | toLowerCase() | Converts all of the characters in this String to lower case using the rules of the default locale. |
| String | toLowerCase(Locale locale) | Converts all of the characters in this String to lower case using the rules of the given Locale. |
| String | toString() | This object (which is already a string!) |
| String | toUpperCase() | Converts all of the characters in this String to upper case using the rules of the default locale. |
| String | toUpperCase(Locale locale) | Converts all of the characters in this String to upper case using the rules of the given Locale. |
| R | transform(Function<? super String,? extends R> f) | This method allows the application of a function to this string. |
| String | translateEscapes() | Returns a string whose value is this string, with escape sequences translated as if in a string literal. |
| String | trim() | Returns a string whose value is this string, with all leading and trailing space removed, where space is defined as any character whose codepoint is less than or equal to 'U+0020' (the space character). |
| static String | valueOf(boolean b) | Returns the string representation of the boolean argument. |
| static String | valueOf(char c) | Returns the string representation of the char argument. |
| static String | valueOf(char[] data) | Returns the string representation of the char array argument. |
| static String | valueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count) | Returns the string representation of a specific subarray of the char array argument. |
| static String | valueOf(double d) | Returns the string representation of the double argument. |
| static String | valueOf(float f) | Returns the string representation of the float argument. |
| static String | valueOf(int i) | Returns the string representation of the int argument. |
| static String | valueOf(long l) | Returns the string representation of the long argument. |
| static String | valueOf(Object obj) | Returns the string representation of the Object argument. |
nombre = nombre.toUpperCase();
System.out.println("Mayúsculas : "+nombre);
nombre = nombre.toLowerCase();
System.out.println("Minúsculas : "+nombre);
int indice = nombre.indexIf('F');
System.out.println("Indice encontrado: "+indice);
char letra = nombre.chartAt(indice);
System.out.println("Caracter en indice(%s) encontrado: %c", indice, letra);
Formato de Strings
| Format Specifier | Data Type | Output or Return value |
|---|---|---|
| %a | floating point | Returns a Hex output of floating point number |
| %b | Any type | True or False |
| %c | character | Unicode character |
| %d | integer | Decimal Integer |
| %e | floating point | a decimal number in scientific notation |
| %f | floating point | decimal number |
| %g | floating point | decimal number, possibly in scientific notation depending on the precision and value |
| %h | Any type | Hex String of value from hashCode() method |
| %n | None | Platform-specific line separator |
| %o | integer | Octal number |
| %s | Any type | String value |
| %t | Date/Time | %t is the prefix for Date/Time conversions |
| %x | integer | Hex string |
StringBuilder
String texto = "Ayuda";
texto = texto.concat("-");
texto = texto.concat("me ");
texto = texto.concat("subí ");
texto = texto.concat("al ");
texto = texto.concat("bus ");
texto = texto.concat("equivocado ");
System.out.println(texto);
Esto no es bueno pensando en el rendimiento. Para esto existe la clase StringBuilder que ayuda a concatenar Strings de manera más eficiente.
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("Ayuda");
builder.append("-");
builder.append("me ");
builder.append("subí ");
builder.append("al ");
builder.append("bus ");
builder.append("equivocado ");
String texto = builder.toString();
System.out.println(texto);
StringBuilder es una clase común. Se utiliza new para crear el objeto, mutable, (usa la misma referencia, sin nuevas asignaciones). E implementa la interfaz CharSequence. Es decir, algunos métodos de la clase String con comunes con StringBuilder.
System
Note
Métodos staticos son accesibles sin requerir una instancia
Object
Clase principal de java, todos los objetos heredan de Object
package com.bytebank.test;
import com.bytebank.modelo.CuentaAhorro;
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String nombre = "DevFzn";
nombre = nombre.replace('D', 'd');
nombre = nombre.concat(" estudiando con Alura");
System.out.println(nombre);
printLine(nombre);
printLine(nombre.indexOf("F"));
printLine(nombre.charAt(3));
printLine(new CuentaAhorro(11, 22));
}
public static void printLine(Object valor) {
System.out.println(valor.toString());
}
// Sobrecargando método printLine()
public static void printLine(String msj) {
System.out.println(msj);
}
public static void printLine(int valor) {
System.out.println(valor);
}
public static void printLine(char caracter) {
System.out.println(caracter);
}
}
...
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("Cuenta\nNro : %d\nAgnc : %d", this.numero, this.agencia);
}
...
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
Output
devFzn estudiando con Alura
devFzn estudiando con Alura
3
F
Cuentas creadas: 1
Cuenta
Nro : 22
Agnc : 11